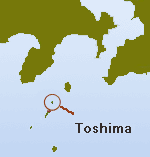
The seeds used for our camellia oil are harvested on Toshima island, which is located about 100_miles south of Tokyo. Though only 300 people live on this one-acre island, it is covered with Camellia Japonica trees and produces nearly 60% of the camellia oil in Japan.

Toshima

Camellia Japonica trees

Camellia Japonica
 Hair care
Hair care
Camellia oil supplies nutrients to the scalp and gently protects hair using natural ingredients that do not easily oxidize or deteriorate. This oil supplies rich moisture and elasticity to soften the hair. It is very effective on stiff hair. For best results this oil should be applied when the hair is damp (for example, after a shower).
 Skin care
Skin care
For care of dry skin, rough skin and sun-burnt skin, this oil replenishes the same natural nutrients of the sebum and makes the skin smooth. It increases the metabolism of the skin and supplies moisture, increasing firmness, so the skin remains both beautiful and youthful. It blocks ultraviolet rays and combats blotches and freckles. Also, for skin care after shaving, it is perfect as an after-shave lotion.
In our skin, there is a certain type of oil called sebum derived from the epidermis cells and secreted from the hair glands. Water secreted from the sweat glands is mixed with the oil on the surface of the skin to create a moisture barrier. This gives our skin protection from the air. A moisture barrier prevents the penetration of the weather and toxic substances and acts to neutralize acid and alkali.
The outermost skin layers usually retain 10% to 20% of this moisture barrier. Gradually, this retained moisture has an emollient effect, lending an antiseptic action, inhibiting evaporation, and so on. The amount of sebum retained in the skin reaches a peak when a person is twenty years old on average and then decreases. After the age of twenty the skin can rapidly become dry, and it is less easy to regulate its natural oil and moisture content.
Triglycerides are the most stable and the least deteriorating lipid among the lipids secreted from the hair glands. Camellia oil works well and is mild on the skin because a major component of camellia oil is oleic acid triglycerides. It is known that camellia oil contains about 85% oleic acid triglycerides, which is the same as a person's natural sebum. This exceeds the triglyceride level of olive oil, 75%. On this basis, natural camellia oil is the most suitable replacement for sebum to care for your skin.
Camellia oil as a skin-care cosmetic has the following attributes:1.Emollient
This means, "to soften the skin." Camellia oil works quite effectively. If you apply it to your heel, you will experience the softening attributes of the oil.
2.Sun Block
Camellia oil can be used as a sunscreen for sea bathing because it has a strong ultraviolet absorption blocking attributes. For sunblock, please use only colorless camellia oil. Ultraviolet radiation reaching the Earthfs surface is divided into two types, UVA and UVB. UVA is also called the "everyday ultraviolet radiation" and has a long wavelength. It penetrates at the depth of the skin to cause wrinkles and sagging of the skin. UVB is also called the "leisure ultraviolet radiation." It has a short wavelength and is more powerful, causing reddening and inflammation (sunburn). It is also the cause of blotches, freckles, and carcinogens that lead to skin cancer. Please note, Camellia oil protects from UVB but not from UVA.
This oil supplies the right type of oil where it is needed. It works well on skin that has less natural oil such as rough or dry skin. Also, if men use this oil after shaving, the oil will condition the skin and its antiseptic effect will help prevent razor burn.
The Western name "Camellia"The Western name for this flower is "Camellia" (Kamelie in German, Camelia in French). It was originally named after the missionary Georg Joseph Kamel, a Bohemian. He introduced Eastern Asian plants into the Philippines. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus (1707-1778)_named this genus "Camellia" in commemoration of Kamel, then named the species "Japonica," simply meaning "from Japan."
- products
- description
- faq
- information
- contact us
- camellia oil top